The printing plate is an important element in printing technology and is mainly used in flat printing such as offset printing. It contains printing and non-printing areas and transfers the printing information to the printing material. This is usually done indirectly, i.e. via a rubber blanket cylinder. The print motif is the correct way round on the printing plate, reversed on the rubber blanket, and the correct way round again on the paper.
Modern printing plates are usually made of anodised aluminium with a light-sensitive coating. This coating is directly exposed to a laser in a process known as computer-to-plate (CTP). The image information from digital data is precisely transferred to the plate. Films and analogue copying processes are now almost obsolete; films are only used for screen printing (e.g. by filmbelichtung24.de – only available in German). After exposure, the plate is either chemically developed or, in process-free systems, prepared directly for printing.
The key properties of a printing plate are good ink acceptance, high dimensional stability and register accuracy. It must also offer sufficient stability to ensure a consistently good print image, even with high print runs. Its service life depends not only on the material, but also on the dampening solution used, the printing inks and the machine control.

The most important colour management event takes place every two years in Munich: the Fogra Colour Management Symposium. Once again this year, all professionals are invited to make the pilgrimage to Munich: two days of lectures, discussions and a Bavarian evening await participants. Matthias Betz, owner of proof.de, will also be there again: for many years, he has been taking advantage of the opportunity to exchange ideas with colleagues and friends, learn about new technologies, hardware and software, and talk to colleagues from Fogra, freieFarbe, GMG and many more. In … read more
Anyone who has reinstalled or updated their i1 Profiler app in the last few weeks has been confronted with disturbing news: X-Rite announced directly in the start window that it would no longer support its enormously popular i1Display and i1Pro2 devices. Users of the i1Pro 2 devices and i1iO 2 tables, which are extremely popular in printing and colour management, will be particularly hard hit by the announcement: An investment of €6,000 is quickly consigned to the electronic scrap heap. But what can you do if you own such a … read more

Today I received an email in which PANTONE asked how it should orientate its products and services in the future. The users were asked which countries, industries and company sizes they come from, but also what PANTONE products should look like in the future and what customers would be prepared to pay for PANTONE services in the future. Question: How much can PANTONE services cost? PANTONE appears to be orientating itself on the PANTONE Connect prices: All price queries have the lowest price category < $ 7,- / month, i.e. … read more

Adobe products are ideal for image retouching and layout and handle RGB and CMYK colour profiles very well. However, when editing and retouching grayscale images, for example for a black-and-white photo book, the experience is quite different. Suddenly, images look completely different in InDesign than they do in Photoshop, and even when exporting the image to PDF, greyscale images are suddenly treated differently. This article explains where the problems lie with black-and-white images and greyscale profiles in InDesign and Photoshop layouts, and how you can work in a more ‘colour-accurate’ … read more

After Eddy Hagen pointed out in this posts, that there were some major colour deviations between the brand new PANTONE Solid Coated Guide 2023 and the previous version especially for the PANTONE 2635 C, I was curious to lookup the same colours in the new PANTONE Color Bridge Coated Guide of 2023 and compare the colours with the previous version. I measured a dE00 of 8,15 between the two colours that Eddy mentioned, which is really far apart from how accurate PANTONE colours should match between the different PANTONE guides. … read more

A new generation of colour measuring devices is entering the market: in contrast to the classic measuring devices, which are available as a fully encapsulated system either as a colourimeter or as a spectrophotometer, and then supply the data to a computer via an interface or app or display it directly, the new generation of colour measuring devices consist only of lighting and software, with the optics of a modern iPhone from Apple being used as the sensor. Until now, there have been two categories of measuring devices on the … read more
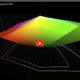
RGB colour spaces are colour systems that represent different hues with the three primary colours red, green and blue. RGB colour spaces are used in digital image processing, photography and computer technology to precisely define colours. The most important RGB colour spaces and their special features are: sRGB sRGB is the most widely used RGB colour space and is used by most monitors, printers and digital cameras. It was developed by HP and Microsoft in the 1990s to create a standard for colour representation on the internet and on various … read more

Whether it’s a large global corporation or a small company, the following often applies to designs or redesigns today: we develop everything for digital first.

In recent weeks, there have been lengthy discussions on the Fogra digital printing mailing list as to whether a research project should be launched to define standardised tonal value gradations for spot colours. What is this all about? In the field of CMYK and seven-colour printing, the definition of clear, printable and proofable standards is well established and has been tried and tested in practice. If the paper or paper class is known and defined, a measuring standard such as M0/M1/M2 has been established and the content of optical brighteners … read more

This year we once again created proofs for Fogra certification and sent them to Munich-Aschheim for testing. With these proof prints, which we print according to three different proof standards and on three different papers, we point out that we not only deliver excellent proof quality through internal quality controls and checks, but that the quality of our proofs is also measured and confirmed by external experts. We have now had test prints certified by Fogra for the 12th time. We have also been “Spot-cert” certified for the display of … read more










