CAT stands for Cromatic Adaptation Transform.
Chromatic adaptation means that the human eye performs an automated white balance. Colour is thus perceived by the human observer quite independently of the colour temperature; a white shirt looks the same white to us under fluorescent light as it does under incandescent lighting, a red rose is similarly red to humans under both lights.
The Cromatic Adaptation Transform (CAT) is a mathematical process in colour processing that simulates the adaptation of colour perception to different light sources. It is based on the natural phenomenon of colour adaptation, in which the human eye adapts to changing light conditions as described above in order to perceive colours consistently. In digital image processing, CAT is used to transform the colours of an image so that they appear constant under different lighting situations such as natural or artificial light.
CAT is used in colour science and image processing to harmonise the colour representation on different devices such as cameras, monitors or printers and to ensure uniform colour perception. For this purpose, the colour values are adapted to the conditions of a reference light source, usually the standard illuminant D65.
The most common CAT models, such as Bradford and von Kries, use different mathematical approaches to calculate the light adjustment. This process is particularly important in digital photography, for the colour calibration of devices and in image processing in order to ensure precise and consistent colour reproduction.
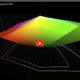
RGB colour spaces are colour systems that represent different hues with the three primary colours red, green and blue. RGB colour spaces are used in digital image processing, photography and computer technology to precisely define colours. The most important RGB colour spaces and their special features are: sRGB sRGB is the most widely used RGB colour space and is used by most monitors, printers and digital cameras. It was developed by HP and Microsoft in the 1990s to create a standard for colour representation on the internet and on various … read more

Today I received an email in which PANTONE asked how it should orientate its products and services in the future. The users were asked which countries, industries and company sizes they come from, but also what PANTONE products should look like in the future and what customers would be prepared to pay for PANTONE services in the future. Question: How much can PANTONE services cost? PANTONE appears to be orientating itself on the PANTONE Connect prices: All price queries have the lowest price category < $ 7,- / month, i.e. … read more

Over the last few months, we at Proof.de have been thinking about further improving our already very good colour measurement technology in terms of speed and measurement precision. Relatively quickly it became clear that only two devices would come into question: The KonicaMinolta MYIRO-9, the successor of the former FD-9, or the X-Rite ISIS 2 XL. The starting point: Since we at Proof GmbH have 5 proofing devices, the calibration of targets for profile optimisation is a time-critical undertaking for us. Therefore, we had been looking around for an upgrade of … read more

Several errors have crept into the new PANTONE 2023 fan decks. In both the PANTONE Solid Coated and the Solid Uncoated color fans, there are colours for which the new ink formulations are incorrect. In the PANTONE Formula Guide Solid Coated fan 2023, PANTONE 107 C and PANTONE 108 C have absolutely identical ink recipes, as well as PANTONE 113 C and PANTONE 114 C. As the colors differ, this cannot be the correct. Several errors in the PANTONE Solid Uncoated fan 2023 In the PANTONE Solid Uncoated fan 2023 … read more
From now on, it’s much easier and faster: in the Proof Shop, you can call up and reorder entire orders or individual proofs directly from your order history. This saves you from having to re-enter every detail and gives you the assurance that all settings will be exactly the same as last time. With just a few clicks, your proofs are reordered – reliably, easily and in no time at all. What exactly is new? You can find your order history in your customer account. There are two new options … read more

In recent years, various problems have arisen with our previous proof paper supplier. On the one hand, we sometimes had to wait more than three months for paper deliveries; on the other hand, we sometimes had significant problems with batch-to-batch discrepancies, surface defects and much more. After lengthy deliberations, we decided in December to replace all the paper. We therefore received pallets of new paper at the turn of the year, which we are now gradually incorporating into our production. There will be no hard cut, but the new papers … read more

Adobe products are ideal for image retouching and layout and handle RGB and CMYK colour profiles very well. However, when editing and retouching grayscale images, for example for a black-and-white photo book, the experience is quite different. Suddenly, images look completely different in InDesign than they do in Photoshop, and even when exporting the image to PDF, greyscale images are suddenly treated differently. This article explains where the problems lie with black-and-white images and greyscale profiles in InDesign and Photoshop layouts, and how you can work in a more ‘colour-accurate’ … read more

Even almost 9 years after the introduction of the successor colour space PSOCoatedV3, ISOCoatedV2 / FOGRA39 is still the most widespread colour space in Europe. We at Proof GmbH count around 200 jobs from time to time for the German Printing and Media Industries Federation, among others. In the last count, proofs in ISOCoatedV2 accounted for around 68% of all proof jobs at our company. This is a clear sign of the continued widespread use of the colour space. ISOCoatedV2: From the classic colour space to the beacon of the … read more

Digimarc is a digital watermark that can be used to embed information in images, videos or other media. Digimarc watermarks are invisible to the human eye, but remain recognisable to special software or devices. Digimarc is becoming increasingly popular in the packaging sector in particular, as this technology allows the digits of the EAN barcode and more to be applied invisibly to all areas of the packaging. Digimarc and EAN barcode at the supermarket checkout When scanning at the checkout, the checkout staff do not have to search for the … read more

The most important colour management event takes place every two years in Munich: the Fogra Colour Management Symposium. Once again this year, all professionals are invited to make the pilgrimage to Munich: two days of lectures, discussions and a Bavarian evening await participants. Matthias Betz, owner of proof.de, will also be there again: for many years, he has been taking advantage of the opportunity to exchange ideas with colleagues and friends, learn about new technologies, hardware and software, and talk to colleagues from Fogra, freieFarbe, GMG and many more. In … read more









